In this section, we answer these questions and show you common examples of injection molded parts to help you familiarize yourself with the basic mechanics and applications of the technology.
What is injection molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing technology for the mass-production of identical plastic parts with good tolerances. In Injection Molding, polymer granules are first melted and then injected under pressure into a mold, where the liquid plastic cools and solidifies. The materials used in Injection Molding are thermoplastic polymers that can be colored or filled with other additives.
Almost every plastic part around you was manufactured using injection molding: from car parts, to electronic enclosures, and to kitchen appliances.
Injection molding is so popular, because of the dramatically low cost per unit when manufacturing high volumes. Injection molding offers high repeatability and good design flexibility. The main restrictions on Injection Molding usually come down to economics, as high initial investment for the mold is required. Also, the turn-around time from design to production is slow (at least 4 weeks).
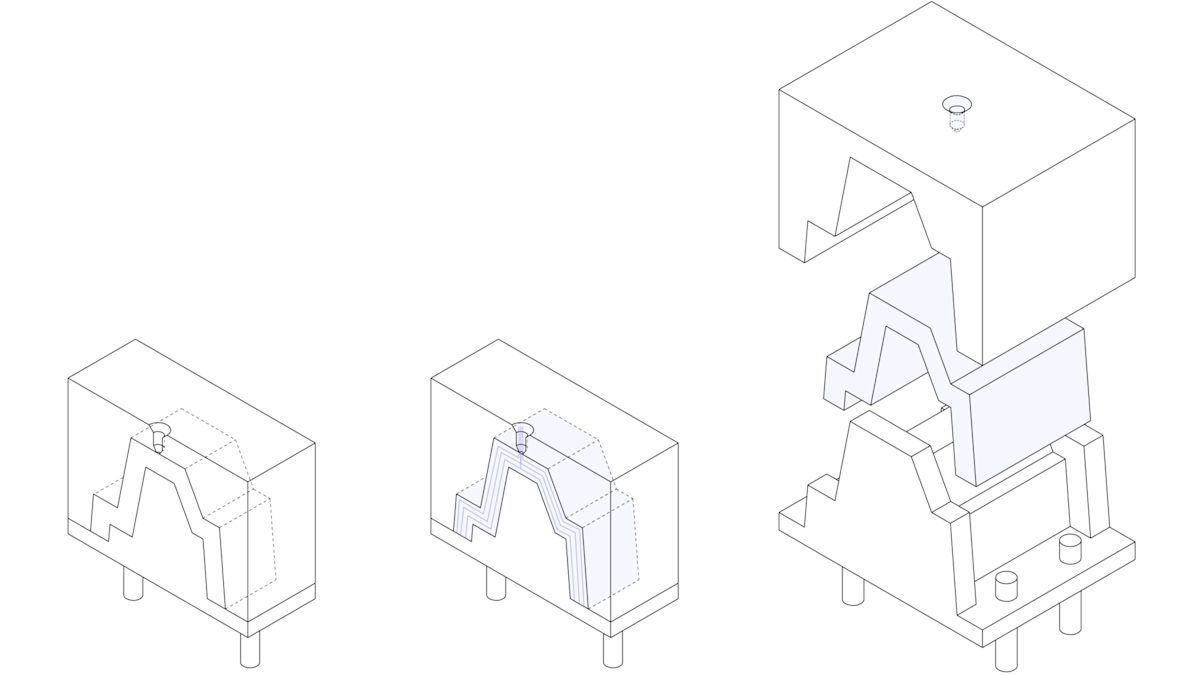
The injection molding process
Injection molding is widely used today for both consumer products and engineering applications. Almost every plastic item around you was manufactured using injection molding. This is because the technology can produce identical parts at very high volumes (typically, 1,000 to 100,000+ units) at a very low cost per part (typically, at $1-5 per unit).
But compared to other technologies, the start-up costs of injection molding are relatively high, mainly because custom tooling is needed. A mold can cost anywhere between $3,000 and $100,000+, depending on its complexity, material (aluminum or steel) and accuracy (prototype, pilot-run or full-scale production mold).
All thermoplastic materials can be injection molded. Some types of silicone and other thermoset resins are also compatible with the injection molding process. The most commonly used materials in injection molding are:
Polypropylene (PP): ~38% of global production
ABS: ~27% of global production • Polyethylene (PE): ~15% of global production • Polystyrene (PS): ~8% of global production
Even if we take into account all other possible manufacturing technologies, injection molding with these four materials alone accounts for more than 40% of all plastic parts produced globally every year!
Copyright © 2025Yuyao Hansheng Electrical Appliances Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Links Sitemap RSS XML Privacy Policy